SQL Server agent job is a windows service based scheduler. Agent job is used to schedule and automate SQL scripts, administrative tasks, SSIS packages and various other tasks using SQL agent job tool. This component is integrated along with SSMS and available under Object explorer as SQL Server Agent.
Scheduling tasks like automatic daily backups, index maintenance, backup and recovery, SSIS packages is possible through a SQL agent job. We can create a scheduled job using agent job UI within SSMS or add it using SQL queries with the help of system stored procedures. For example, we can schedule a daily backup job at late night when business is not running. Above all, an agent job can notify you of the success and failure of information through notifications and alerts.
SQL agent job works as a window service, thus in case it’s disabled by default – you may turn it on. In this tech-recipes post, we are learning to use in-built stored procedures from msdb database to create an Agent job to schedule a stored procedure, daily, in every 10 minutes interval.
Points to Ponder – SQL Agent Job
1.List of jobs available in “Jobs” folder, under SQL Server Agent in SSMS.
2.Primary selections available with a scheduled job are name, steps, schedule, alerts and notifications.
3.Agent job can schedule an ad-hoc SQL query, SSIS package, stored procedure, PowerShell script and various other objects.
4.msdb – a system database stores all the agent job-related configuration.
5.In case agent job is disabled, try to turn on SQL Server Agent (InstanceName) from services.msc as well as from SSMS object explorer.
Components of SQL Agent Job
1.General – We can specify job name, owner, category and description.
2.Steps – A job may have one or more steps. Each step contains one or more tasks. In case we have to schedule the backup of a database A and database B. We can create multiple steps in a single job to achieve this. Below steps, we can specify Ad-hoc SQL query, stored procedure, or SSIS package name. Moreover, failure scenarios and logging can be done under Steps.
3.Schedules – Following schedules, we can specify the date and time to run a job. Different scheduling options are available as per our requirement. Be it daily, weekly or yearly.
4.Alerts & Notification – Different types of alerts and notifications through email can be sent on completion or failure of Agent job as per our requirement.
Create SQL Agent Job Using T-SQL Script
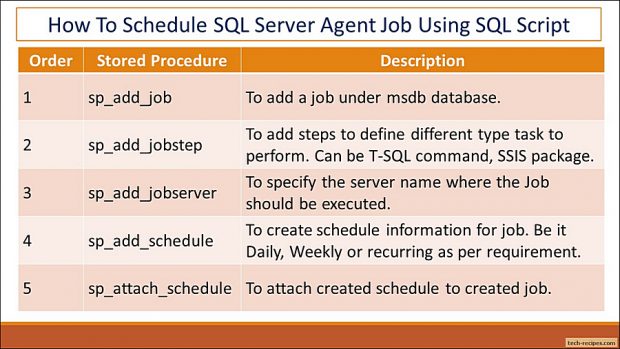
Let’s use different msdb stored procedures to create a SQL agent job using T-SQL queries instead of using GUI.
1
Create a SQL Agent Job.
Using sp_add_job we create a new job. Make sure to note down the Job name specified. We will be using the identical Job name in next stored procedures to add more option to this job.
--Add a Job to SQL Server Agent USE msdb; GO EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_add_job @job_name = N'Daily - Insert Test Job'; -- the job name GO
2.
Add a Step to SQL Agent Job
Adding a step to the created job using sp_add_jobstep. We have specified that running T-SQL query – in short calling a stored procedure that will insert a row in TestSQLJob table. Included database name as well.
USE msdb; GO EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_add_jobstep @job_name = N'Daily - Insert Test Job' -- Job name specified in sp_add_job ,@step_name = N'Step - Set database to read only' -- step name ,@subsystem = N'TSQL' -- Type of step (T-SQL/ SSIS/ etc) ,@database_name = 'AdventureWorksLT2016' --Database Name ,@command = N'EXEC Insert_TestSQLJob;' -- SQL Command GO
3.
Attach Server Name to Job Name
Option to specify the server name where the job will be executed using sp_add_jobserver. You can use the Instance name which you are usign while connecting to your server through SSMS.
--Attach server name. Not needed if you are creating job on same server. EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_add_jobserver @job_name = N'Daily - Insert Test Job' ,@server_name = 'DESKTOP-23ATANB\SQLSERVER17'; -- LOCAL by default GO
4.
Add a Schedule to Job
Scheduling a job through T-SQL requires to understand different parameter available using sp_add_schedule. Please visit MSDN documentation to understand them clearly. Using the below query we have scheduled our job to run Daily, every 10 minutes with no end date. This job will be effective as soon as we create it.
USE msdb GO EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_add_schedule @schedule_name = N'Daily - Every 10 Minutes' -- specify the schedule name ,@freq_type = 4 -- 4 indicates job is scheduled daily, refer msdn link for reference ,@freq_interval = 1 -- The days that a job is executed and depends on the value of ,@freq_subday_type = 4 --At specified time (At specific time/second/minutes/hours) ,@freq_subday_interval = 10 --Run every 10 minutes once the job is scheduled ,@freq_recurrence_factor = 1 --Recurring job GO
5.
Attach schedule to Job
While creating schedule we don’t specify the job name thus required to do it with sp_attach_schedule. Let’s attach our created schedule to the SQL agent job.
--Attach Created Job name to Schedule name Use msdb GO EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_attach_schedule @job_name = N'Daily - Insert Test Job' -- Job Name ,@schedule_name = N'Daily - Every 10 Minutes' ; -- Schedule Name GO
Summary
As a result, we have learned how to add SQL Server agent job using T-SQL Scripts. We have used system stored procedures from msdb database. We can create a SQL agent job from SSMS GUI as well. If you like this post, you may like to browse through tech-recipes database archive.