Many times developers need to implement pagination on search results. Pagination is the process of dividing the results of a query into discrete numbered pages.
SQL Server 2012 has introduced a new and easy method to implement pagination using OFFSET and FETCH NEXT. This process is actually faster compared to previous complex methods like using row_number. This feature is somewhat similar to the MySQL Limit/Offset clause.
OFFSET: specifies the number of rows to skip before it starts returning rows
FETCH NEXT: the number of rows to display in the result
Let us explore Order By Offset fetch in SQL Server 2012 with examples.
Create a table called COMPANY, and populate it with some data.
IF OBJECT_ID('COMPANY') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE COMPANY
GO
CREATE TABLE COMPANY
(
ID INT PRIMARY KEY,
NAME VARCHAR(25),
LOCATION VARCHAR(25)
)
GO
INSERT INTO COMPANY
VALUES (1,'HCL','London'),
(2,'HP','Bangalore'),
(3,'Microsoft','Bangalore'),
(4,'Infosys','Pune'),
(5,'Google','London'),
(6,'GE', 'London'),
(7,'AltiSource','New York'),
(8,'Facebook','Palo alto'),
(9,'IBM','New York'),
(10,'TCS','Mumbai')
GO
SELECT * FROM COMPANY
GOProblem 1.1 – Using only OFFSET
SELECT ID, NAME, LOCATION
FROM COMPANY
ORDER BY ID
OFFSET 3 ROWSIn the query above, we are using only OFFSET, so it will skip the first three rows and will return all remaining rows in a determined order.
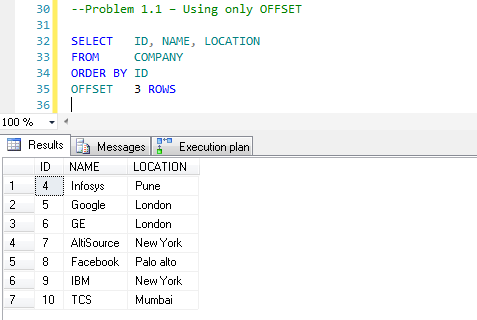
Problem 1.2 – Skip zero rows, and fetch the first five rows.
SELECT ID, NAME, LOCATION
FROM COMPANY
ORDER BY ID
OFFSET 0 ROWS
FETCH NEXT 5 ROWS ONLYIn the query above, OFFSET 0 ROWS means we have skipped zero and FETCH NEXT 5 intends to retrieve the next five rows.
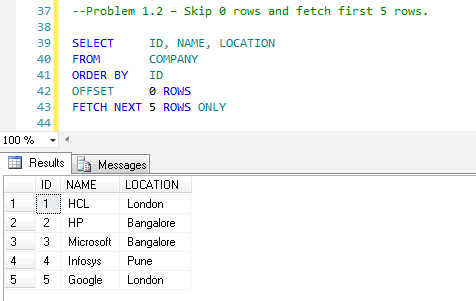
Problem 1.3 – Skip the first five rows, and fetch the next five rows.
SELECT ID, NAME, LOCATION
FROM COMPANY
ORDER BY ID
OFFSET 5 ROWS
FETCH NEXT 5 ROWS ONLYHere, we are skipping the first five rows and fetching the next five rows.
The result above can be achieved using SQL Server 2005/2008 using row_number and derived table.
SELECT ID, NAME, LOCATION
FROM
(
SELECT ID, NAME, LOCATION, ROW_NUMBER() OVER(ORDER BY ID) as rownum
FROM COMPANY c
) DT
WHERE DT.rownum BETWEEN 6 AND 10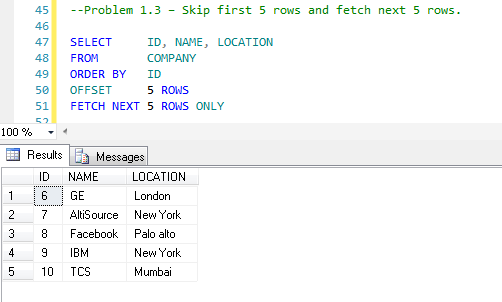
Performance comparison between OFFSET FETCH and ROW_NUMBER
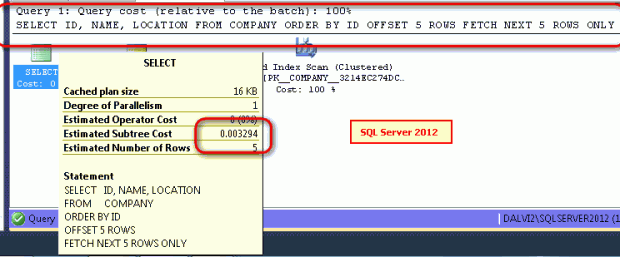
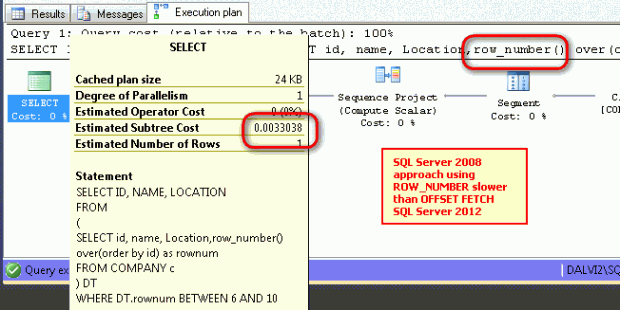
The OFFSET FETCH approach took 0.003294, and the row_number approach took 0.0033038. This shows the newer approach OFFSET FETCH in SQL Server 2012 is faster.
Problem 1.4 – Using Variables with OFFSET and FETCH
DECLARE @OffSetRows AS INT = 5
DECLARE @FetchRows AS INT = 5
SELECT ID, NAME, LOCATION
FROM COMPANY
ORDER BY ID
OFFSET @OffSetRows ROWS
FETCH NEXT @FetchRows ROWS ONLYThis is the same as Problem 1.3, but here we are using variables to store OFFSET and FETCH values.




